
Molecular Modeling
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. Various strategies exist in Molecular Modeling, for example, structure-based drug design (SBDD) using the three-dimensional structure of proteins, ligand-based drug design (LBDD) using the pharmacophoric features of ligand, fragment-based drug design (FBDD) and Denovo Design. An appropriate strategy must be selected according to the target protein. We mainly develop inhibitors for protein kinase that mediates signaling by phosphorylation in living organisms.
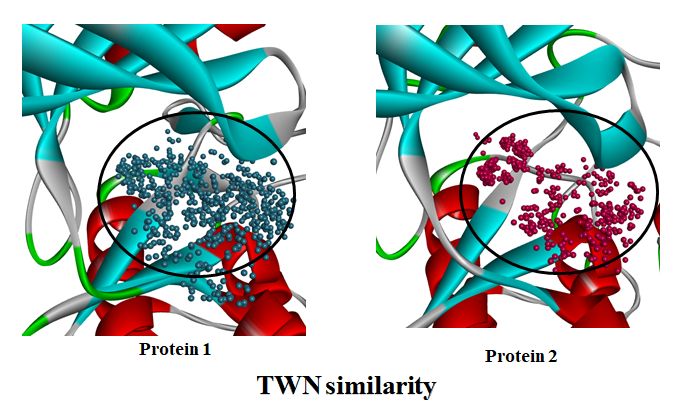
Topological Water Network (TWN)
When a ligand binds to a disease-related target protein, entropy increases as water molecules in the binding site go out. This is called the hydrophobic effect, and the protein-ligand is bound by the thermodynamic process of these water molecules. In the past, computer-based drug design (CADD) research methods considered only proteins or ligands. But recently, studies consider the physicochemical properties of these water molecules more actively.
However most known algorithms require calculation of the total free energy of the system and research is concentrated only on the inner surface of the protein binding site (first layer). Topological water network (TWN) considered that water molecules can be quantified without free energy calculation. TWN can consider not only the protein surface but also the inner (second layer). TWN consists of hydrogen bonds in ring-shaped polygons such as 3-ring, 4-ring, 5-ring, and 6-ring formed among water molecules.
However most known algorithms require calculation of the total free energy of the system and research is concentrated only on the inner surface of the protein binding site (first layer). Topological water network (TWN) considered that water molecules can be quantified without free energy calculation. TWN can consider not only the protein surface but also the inner (second layer). TWN consists of hydrogen bonds in ring-shaped polygons such as 3-ring, 4-ring, 5-ring, and 6-ring formed among water molecules.




TWN RENCOD
TWN RENCOD is a method we developed, which is a tool to calculate protein similarity.
You can test our method by clicking image upside.